What is the Difference Between 4G LTE and 5G Routers?
4G, 5G, LTE Routers – Both 4G long term evolution (LTE) routers and 5G routers enable devices to connect to cellular networks, but they’re designed for different generations of mobile network technology. If you’re wondering how these routers compare, or which type is right for you, read on to see some of the biggest differences between the two.
What is a 4G LTE router?
4G LTE routers connect to 4th generation LTE networks. 4G stands for the fourth generation of mobile network technology, succeeding 3G.
What is a 5G cellular router?
As the successors of 4G LTE, 5G routers connect to the 5th generation technology standard for wireless networks. The term LTE is mainly associated with 4G, while 5G is simply referred to as 5G, without an LTE associated with it. Cellular 5G networks open up new opportunities for higher speeds and lower latencies for everything from mission-critical services to enhanced enterprise networks and Internet of Things (IoT). 5G cellular routers capitalize on these opportunities.
Learn more about 5G cellular routers
How does the technology differ between 4G LTE and 5G?
One of the major differences between 4G LTE and 5G cellular routers are the frequency bands used by each. Frequency bands refer to the range or interval of radio frequencies used to transmit a signal for Internet connectivity.
4G LTE routers use frequencies below 6 GHz, often referred to as sub-6. 5G routers are more flexible than 4G LTE, since they can use low-band frequencies below 6 GHz for long-distance communication and also high-band mmWave frequencies starting at 24 GHz and above. These high-band frequencies offer significant advantages like a rapid increase in speed, ultra-low latency (responsiveness), and more bandwidth (the ability to connect a lot more devices at once).
What are sub-6 and mmWave frequency bands?
The bandwidth of Millimeter waves, also known as mmWave, are frequency bands higher than 24 GHz. Their bandwidths are extremely high, but transmission distances are short. With support from foundation technologies like Small Cell and Massive MIMO, mmWave can overcome short travel distances and obstructions that impair connectivity.
Sub-6 refers to frequency bands under 6 GHz, which includes most LTE bands. Sub-6 bands have similar transmission distances and bandwidths as their LTE-A counterparts (LTE-A is an enhancement of LTE), but offer comparatively faster speed and capacity than LTE networks.
Why do frequency bands matter?
Low-band frequencies (less than 1 GHz) enable greater coverage but lower speeds, mid-band frequencies (1 GHz–6 GHz) balance speed with coverage, and high-band frequencies (24 GHz–40 GHz) have higher speeds but a smaller coverage radius.
Windows and walls can reflect or block high frequency signals, but 5G networks can penetrate building materials by using low-band frequencies. With the ability to transmit across high, mid, and low-band ranges, 5G cellular routers can use different frequencies at different times for the best results. For instance, they can use low-band frequencies below 6 GHz for long distance communication and then switch to high band once the signal is closer to its source destination.
How much faster is 5G than 4G LTE?
4G LTE typically offers peak data rates of 1 Gbps (1 gigabyte per second), though real-world speeds depend on factors like network congestion and signal strength, among other things.
5G networks can offer peak data rates of up to 20 Gbps (20 gigabytes per second). Even in real-world scenarios, 5G can delivers faster speeds than 4G, especially on networks using higher frequency bands like millimeter waves.
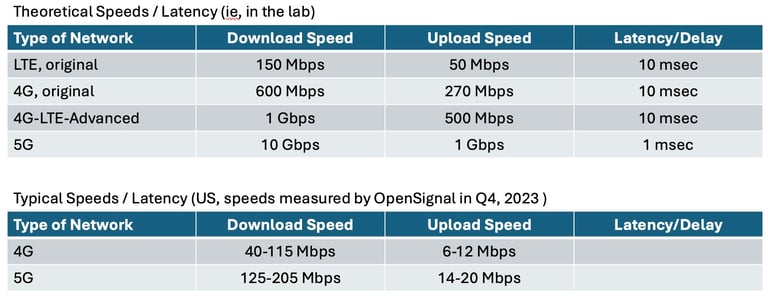
What is the latency difference between 4G LTE and 5G?
The typical latency on a 4G network is around 30-50 milliseconds.
Latency on 5G can be as low as 1 millisecond under specific conditions, which is key for the seamless operation of self-driving cars, telesurgery systems, and critical industrial applications.
What about capacity and connectivity?
4G infrastructure supports fewer simultaneous connections than 5G. 5G increases the number of devices that can be connected simultaneously, making it ideal for densely populated areas and IoT. 5G also supports over 500 times the connection density compared to 4G in a given area without congesting the mobile network. Read more about 5G and IoT.
What about device design and chip sets?
4G wireless routers use 4G modem chipsets, while 5G routers use 5G modem chipsets. 5G chipsets are more complex, as they support a broader range of frequencies and technologies.
Are 5G routers backward compatible?
Many 5G routers are designed to be backward compatible, meaning they can connect to 4G networks when a 5G signal isn’t available.
What applications do 4G LTE and 5G routers support?
4G routers support common online activities like streaming, web browsing, and video conferencing. 5G routers handle all these activities and more. The higher speeds, greater capacity, and lower latency offered by 5G cellular modem routers open the door to more demanding applications and use cases, from mission-critical communications to virtual reality (VR).
Find the right router for your specific needs
If you’re trying to decide between a 4G LTE router or a 5G router, Peplink offers a range of options at different price points. Reach out to us our one of our certified partners to discuss which router is best for your environment and needs.
Explore Peplink cellular routers
.