What’s the best 5G router out there? Understanding the nuances of modern wireless technology to make a decision can be intimidating. With the advent of 5G and other technologies, there are more options and features available than ever before. Here we’ll walk you through the key aspects of 5G routers, to help you make an informed decision for your connectivity needs.
5G is the latest generation of cellular wireless technology
The term “5G” refers to the fifth generation of cellular network technology, and represents the latest generation of mobile cellular communication. 5G networks deliver higher data rates and faster speeds, reduced latency and delay, and increased capacity compared to previous generations.
Is a 5G router the same thing as a 5GHz WiFi router?
When looking for a 5G router, it’s important to understand there’s a difference between a 5G cellular router, which connects your router to the Internet through a cellular network and cell provider (such as T-Mobile, AT&T or Verizon), and 5GHz WiFi or a 5GHz router, which connects your router to your computer or phone in your home or office, over WiFi. Some routers do both of these things!
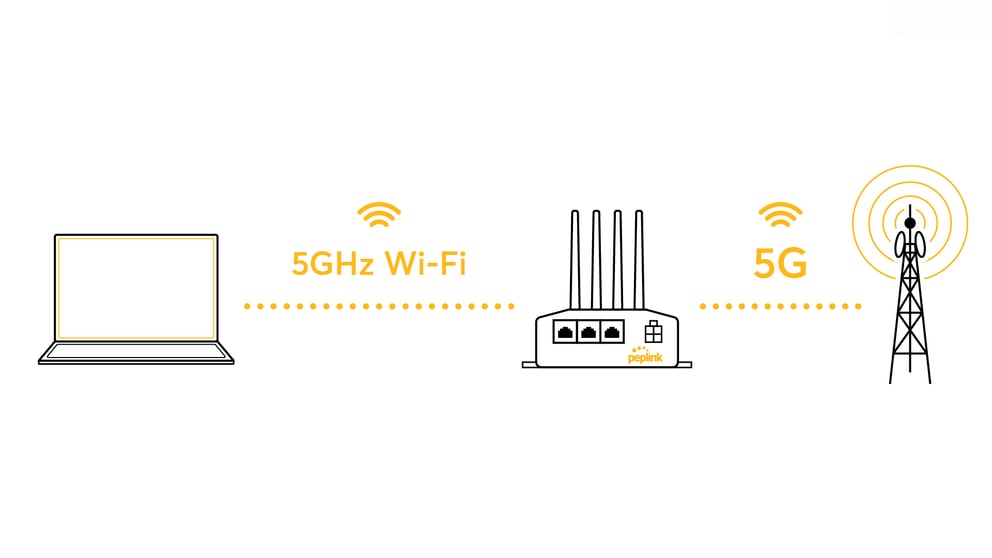
[diagram of router connected to cellular network and laptop over 5G and 5GHz WiFi]
When looking for a 5G cellular router, don’t be confused about references to a “5G WiFi” router – it’s not the same thing.
Why would you want a 5G router?
A 5G router can have many advantages, depending on the application it’s needed for. Some typical applications and benefits where 5G routers can be most useful:
Home or home office use – For consumer or work from home applications, a 5G router works great for:
- Better Internet performance – A 5G router can significantly improve home internet speeds and reliability in areas where traditional broadband connections are limited or unavailable. For example, 5G Internet can have much faster performance than DSL Internet or satellite connections. For gaming and other realtime applications, 5G Internet can have lower delays or “ping times”.
- Backup connection – A 5G router with “dual WAN” capabilities can use a wired connection and a 5G connection together so that the Internet stays up, even when the wired connection goes down. A 5G router running on an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) can maintain Internet connection even when the power goes out, which can cause certain types of traditional Internet (Cable Internet) to go down.
Business Internet use – For business use, 5G routers can deliver:
- More reliable Internet connections – A 5G router with “dual WAN” capabilities can use a wired connection and a 5G connection together so that the Internet stays up, even when the wired connection goes down. A 5G router running on an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) can then maintain Internet connection even when the power goes out.
- Easier installation and setup – 5G routers can be truly plug-and-play, where you simply plug in the router and it connects to the Internet over the 5G cellular network, and creates a local WiFi connection you can use with your local devices such as computers, laptops and mobile devices. There’s no waiting for an installer to run fiber or cable lines to your place of business.
- A reliable backup for fiber optic Internet – Even when you have a fiber optic Internet connection, things can happen that cause you to lose Internet. With a dual-WAN 5G router, your connection can be instantly switched over to the 5G cellular network, keep your business up and running.
Mobile applications – When mobility is needed beyond a fixed location, 5G routers are excellent for:
- RV and work-from-anywhere applications – A mobile 5G router can travel with you, keeping you connected at high speeds. Using multiple SIM cards connected to different carrier networks and external antennas can ensure you maintain connectivity in as many places as possible.
- Marine, boating and yacht applications – On rivers, lakes and near-shore ocean locations, 5G routers with cellular coverage can bring high-speed Internet to passengers and crews on board boats, ships and yachts. Coupled with Starlink satellite connections, many 5G routers such as the Peplink xxx can switch from terrestrial 5G connections to satellite seamlessly, ensuring reliable Internet is always available.
- Telemedicine – 5G networks high-bandwidth capabilities are ideal for remote telemedicine applications where speed and bandwidth are critical, even when teams are far from traditional means to connect to the Internet.
- Emergency services – Ambulances, rescue, and other emergency services applications require fault-tolerant connectivity on the move in “urban canyons” and distant, remote locations. With multi-carrier connectivity, robust multi-SIM 5G routers can ensure teams stay connected.
- Disaster management & recovery – When disaster strikes and traditional networks are down, disaster recovery teams need reliable connectivity under adverse conditions. Even when network equipment is destroyed in disasters, 5G and cellular networks can often be restored quickly, faster than with terrestrial services. Remote teams can then maintain connectivity through 5G routers that may also be connected to satellite systems such as Starlink.
Industrial uses – In an industrial environment, 5G routers support:
- Internet of Things (IOT) applications – 5G is well suited for IoT applications due to it’s high bandwidth, low latency (delay). It’s been designed to support a massive number of connections – thousands to millions – and 5G “network slicing” allows the creation of multiple virtual networks that can be tailored to meet the needs of IoT applications. There are also low-power modes available for battery-powered and remote devices.
- Factory and autonomous robotic applications – With 5G, factory floors are beginning to look at replacing their WiFi networks with private 5G networks, which are designed to scale far more effectively than traditional WiFi. In particular, 5G private networks provide improved scalability to thousands, or even millions, of devices, and are less susceptible to interference than WiFi.
- Monitoring and surveillance – The high-bandwidths available with 5G are particularly suited for high-resolutions monitoring and surveillance. In remote locations, mobile 5G routers can provide robust connectivity for cameras and intrusion detection.
What type of router gives you the fastest connection?
The fastest Internet is usually delivered over Gigabit fiber optic connections to your router or modem, and a wired ethernet connection to your computer – you can get up to 10 Gigabits per second! However, this type of connection is frequently not available, or even convenient (who wants to have a wire running to their laptop or cell phone?)
Below is a comparison table of Internet technologies and speeds, to help in selecting the best router for your needs:
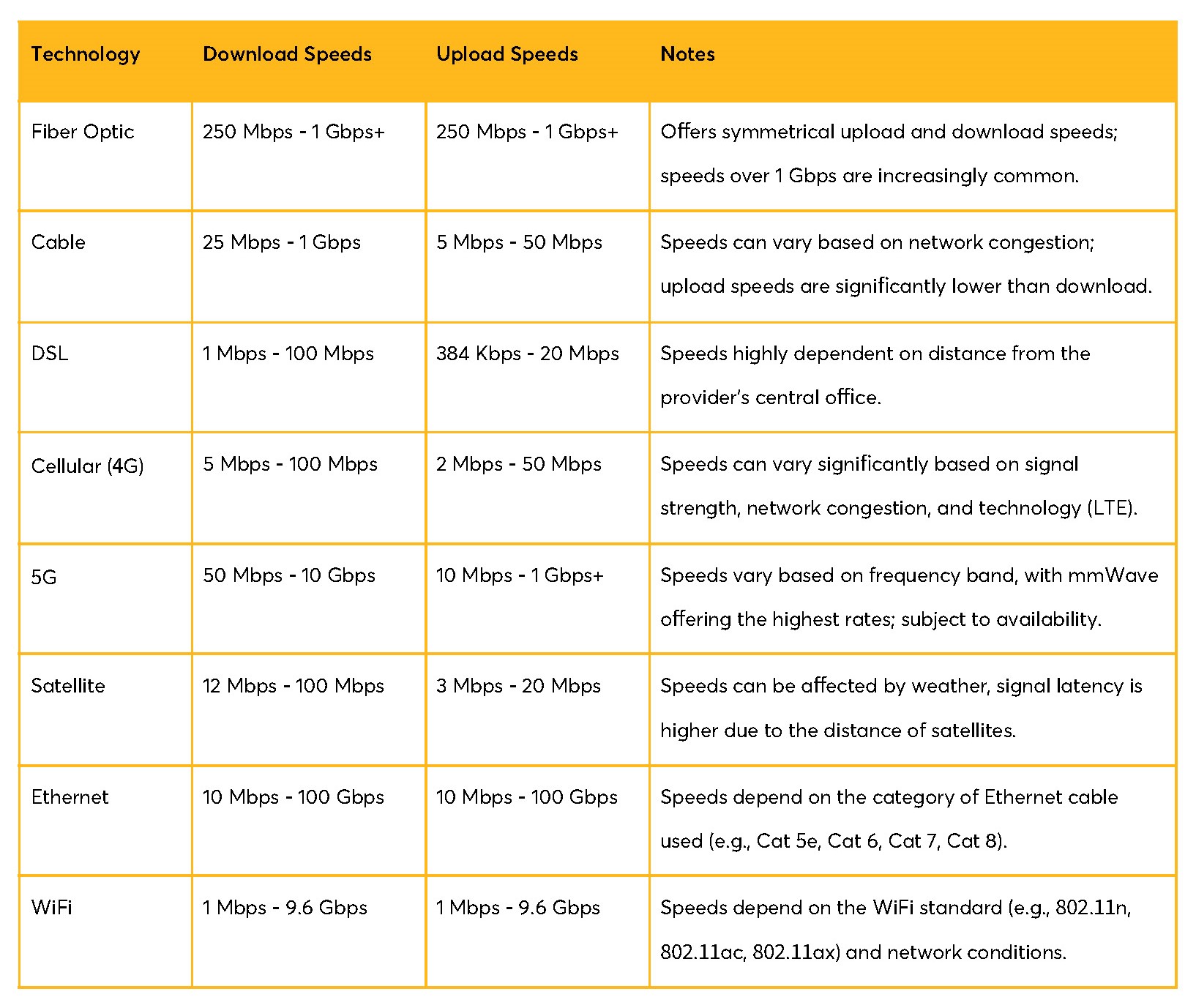
As you can see, a 5G router with WiFi and Ethernet can do really well in delivering very fast Internet speeds!
Do you need a SIM card to use a 5G router?
All cellular technologies, including 5G, use a Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) in their phones, modems, router or hotspots of some sort. The SIM is a small physical card (SIM card) that is plugged in or removed, or stored in the device (eSIM). Because of this, 5G routers may have a SIM card (sometimes called a 5G SIM router or just SIM router), or may just have a built-in eSIM card. Some routers have both, or may have multiple SIM cards that can be connected to different carriers to increase bandwidth, or to provide better reliability in case coverage is not good on one of the carriers. See What is a 5G SIM Router?
What’s the difference between a 5G router and a hotspot?
Both mobile 5G routers and hotspots offer mobile Internet access. Mobile routers are ideal when you need to connect multiple devices, require longer usage, or need additional features. Some dual-WAN 5G routers are configureable to provide automatic backup, or failover, if a primary Internet connections goes down. Hotspots, on the other hand, are better when you need casual, mobile Internet access for a limited number of devices.
Differences between mobile 5G routers and hotspots include coverage and range (routers are better at both), portability (hotspots tend to be smaller and battery-operated), and configurability (routers can be configured for automated and advanced functions, such as firewalls and VPNs, while hotspots tend to be simple, manual devices). See Is a SIM Router better than a Hotspot?
What’s the difference between 5G and 4G or LTE cellular routers?
A 5G router is a cellular router that can connect to 5th-generation cellular networks. 5G is the latest in cellular technologies, representing the fifth network technology generation. 5G cellular technology enables much faster speeds and less delay than 4G cellular technologies.
A 4G router is a cellular router that can connect to 4th-generation cellular networks. 4G is the fourth generation of network technology, introduced starting in 2008 and still in use today. Originally, LTE was a different cellular technology introduced about the same time as 4G, but that didn’t meet the speed requirements of 4G. With advancements, LTE became a true part of 4G in 2010, and today the terms 4G, LTE and 4G LTE are often used interchangeably by manufacturers and carriers. See What is the difference between 4G LTE and 5G Routers?
Do all 5G routers work with all carriers?
All carriers place some restrictions on the equipment they will work with. The major restrictions are:
Carrier Certification
In the US and elsewhere, cellular carriers require 5G routers and other equipment that connects to their networks to be certified. Certification typically involves lab testing of each piece of equipment to ensure it has the required cellular radio performance, network compatibility, SIM and USIM operation with carrier’s SIM cards or eSIM systems and other attributes. Router manufacturers typically list which carriers they are certified to operate with.
Compatibility with service plans
In addition to certification, some carriers limit the data plans that can be “provisioned” (activated) for a given 5G router. For example, a carrier may allow certain devices to only work with business data plans, or may “lock” a router that they provide as a part of a consumer service plan to only function on that specific plan. It’s best to check with your carrier or with other users or online forums to ensure the 5G router you want to use will work with a given carrier’s service plan. There are even specialty providers who will bundle 5G router hardware with service plans that they know will work.
How to choose the best 5G router
Things to Consider – As you evaluate 5G routers, here are some factors to consider:
Connectivity Needs
Network Compatibility and Band Support: Does the cellular router you’re considering support the network technologies and bands used by your cellular carrier? Different regions and carriers may use different frequency bands and technologies. If you’re looking for the ultimate in 5G speed performance, consider what bands your router and network are using:
- Sub-6GHz Bands: The lower-frequency bands below 6GHz are often referred to as sub-6GHz. These bands provide a balance between coverage and data speeds, and are typically used for wider area coverage in urban and suburban environments.
- Mid-Band (C-Band and others): Mid-band frequencies like the C-band are in the range of 2GHz to 6GHz. These frequencies offer a compromise between coverage and capacity, and provide faster data speeds compared to sub-6GHz bands.
- Millimeter Wave (mmWave) Bands: High-frequency bands above 24GHz are called mmWave bands. These bands offer the highest bandwidth, but have a shorter, more limited range to reach from the cellular network (cell site) to your router.
Data Speeds: Consider the maximum data speeds the router can provide. If you need high-speed Internet, opt for a router that supports faster speed 5G connections and frequency bands. Also consider the router’s data throughput, as some routers have faster processing speeds and can handle faster data connections than others.
SIM Card Slots: Some routers allow you to supply your own SIM card or offer dual SIM capabilities, [Link to new What is a multi-SIM router? page] allowing for connection failover or using two different carriers. Consider how many SIM cards you plan to use and make sure the SIM router has enough SIM card slots. Learn more about multi-SIM routers.
Use Cases
Home vs. Travel: If you’re traveling and plan to be away from power sources, a compact router can be essential. If you intend to use the router in your home or office, a larger model with more features (like more Ethernet ports or external antenna connectors) may better suit your needs.
Rural Areas or Large Spaces: In areas with weak signals, consider a router with external antenna connections or multiple antennas built in to boost reception and extend coverage.
Features
Ethernet and USB Ports: Will you be connecting wired devices like computers, smart home appliances or IP cameras, or sharing storage? Make sure your router has all the Ethernet and USB ports you’ll need.
Security Features: VPN support, firewall capabilities, and strong encryption are essential for business users and those concerned about privacy.
Management and Configuration: Some routers offer user-friendly apps or web interfaces for configuration and monitoring. Others allow remote management from a central location using network management software or cloud services.
Price: Cellular routers vary widely in price, so consider your budget and compare options within your price range. More expensive routers tend to have advanced features and better build quality, meaning increased reliability, but there are many budget-friendly options that may also suit your needs.
Additional Features: Some routers come with additional features such as failover capabilities, external storage support, and cloud management. Assess your specific needs to see if these features are important.
Which Brand is Right for You?
Brand Reputation: Established brands often offer better customer support, firmware updates, and have a proven track record of reliability.
Reviews: Industry reviews and user feedback can provide valuable insights into real-world performance, reliability, and any potential issues. For instance, you can see reviews of Peplink 5G cellular routers for business use on Gartner.com.
Future Proofing: If you plan to use your router for several years, consider its potential longevity in the rapidly evolving world of tech. You may want to check its compatibility with upcoming network standards or its software update frequency.
Choosing the Best Router
Ultimately, the best cellular router for you will depend on your unique needs, so evaluate your specific use case and requirements carefully before purchasing a router. At Peplink, we frequently help people determine which router is right for them, so feel free to reach out to us.
Peplink Cellular Routers Power Fast and Reliable Connections Around the World
Contact peplink to learn more about 5G routers
Related Articles: