What is an antenna? Why do we need it?
Anytime you want to connect to the internet wirelessly, you must have an antenna. An antenna is a device that converts electrical signals into radio-frequency power and vice versa. With an optimal antenna, clear signals can be transmitted and received between multiple wireless points, even when you’re on the road or at sea. Installed on a recreational vehicle or marine vessel, antennas can bring users great signal reception.

After realizing the value of antennas in cellular deployments, it’s just as valuable to consider which is the right one for you. This is because they don’t amplify signals or create energy, but help focus the transmission and reception. Mainly, there are two types of antennas, Directional and Omnidirectional.
Directional antennas
Directional antennas are primarily used for stationary installations. They focus weak signals in remote or crowded locations with a lot of noise such as residential, offices, fixed-installation IoT devices and utilities. This type of antenna transmits and receives signals from a specific direction. The receiving pattern of a directional antenna is like a cone.
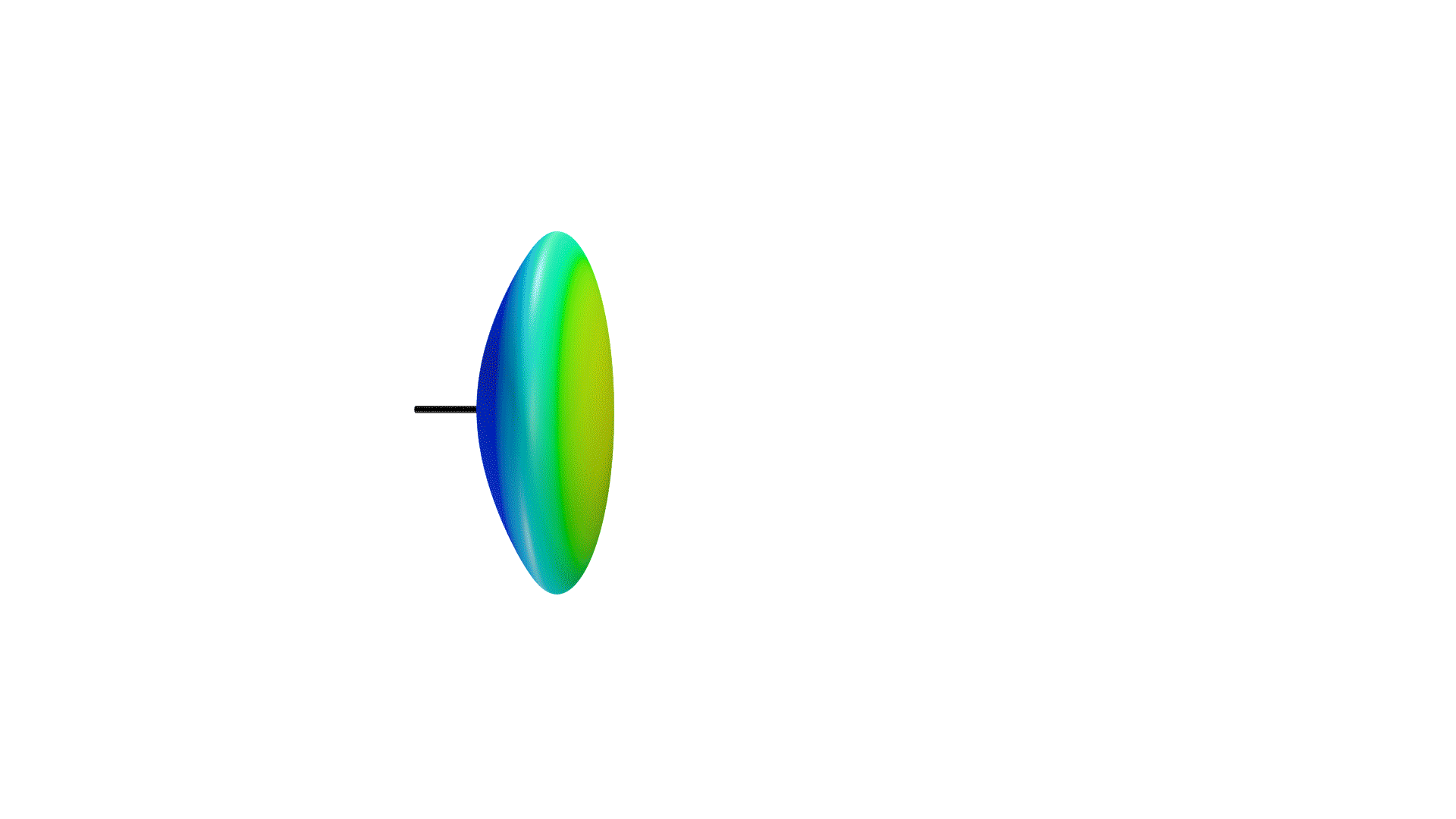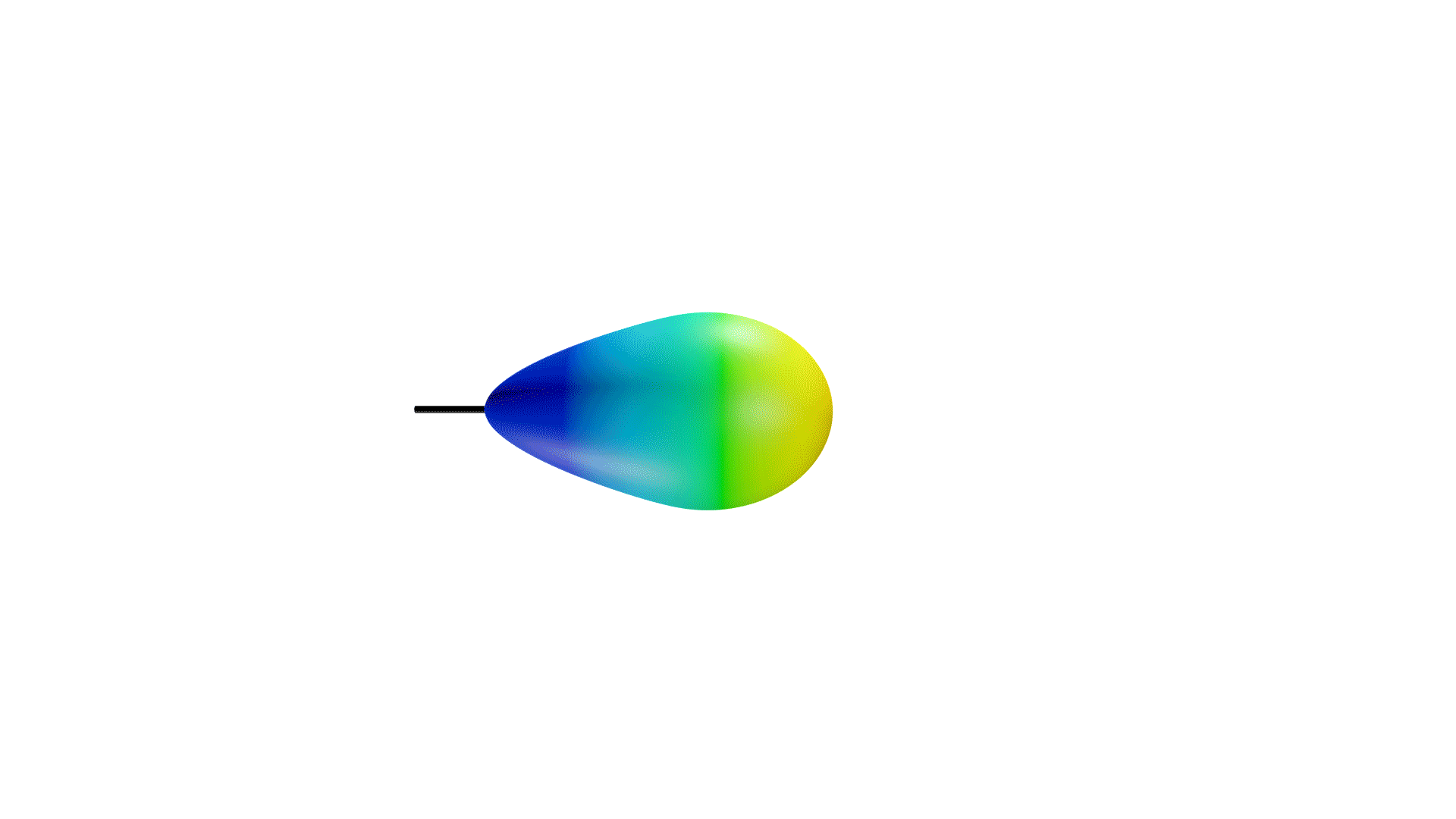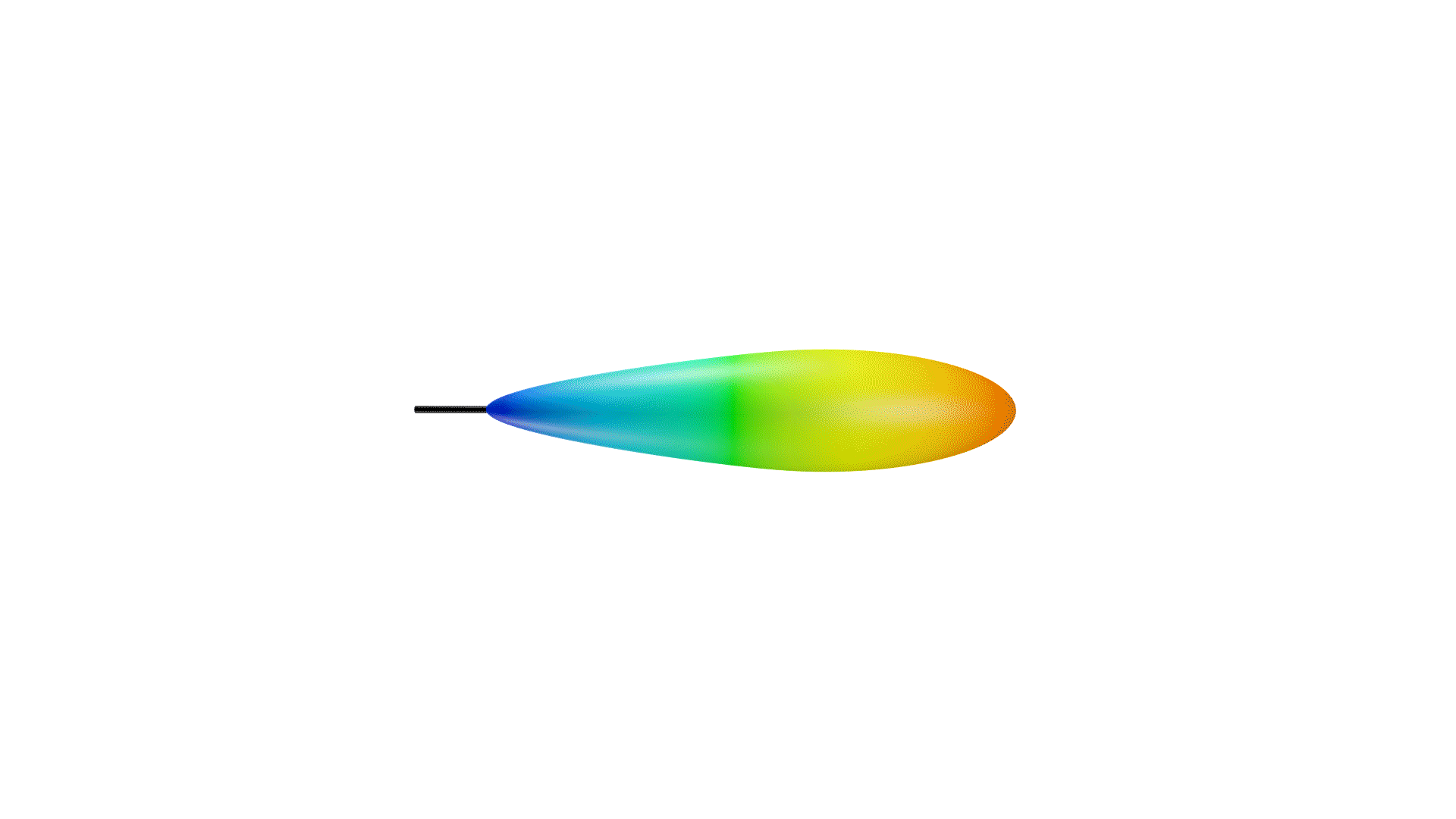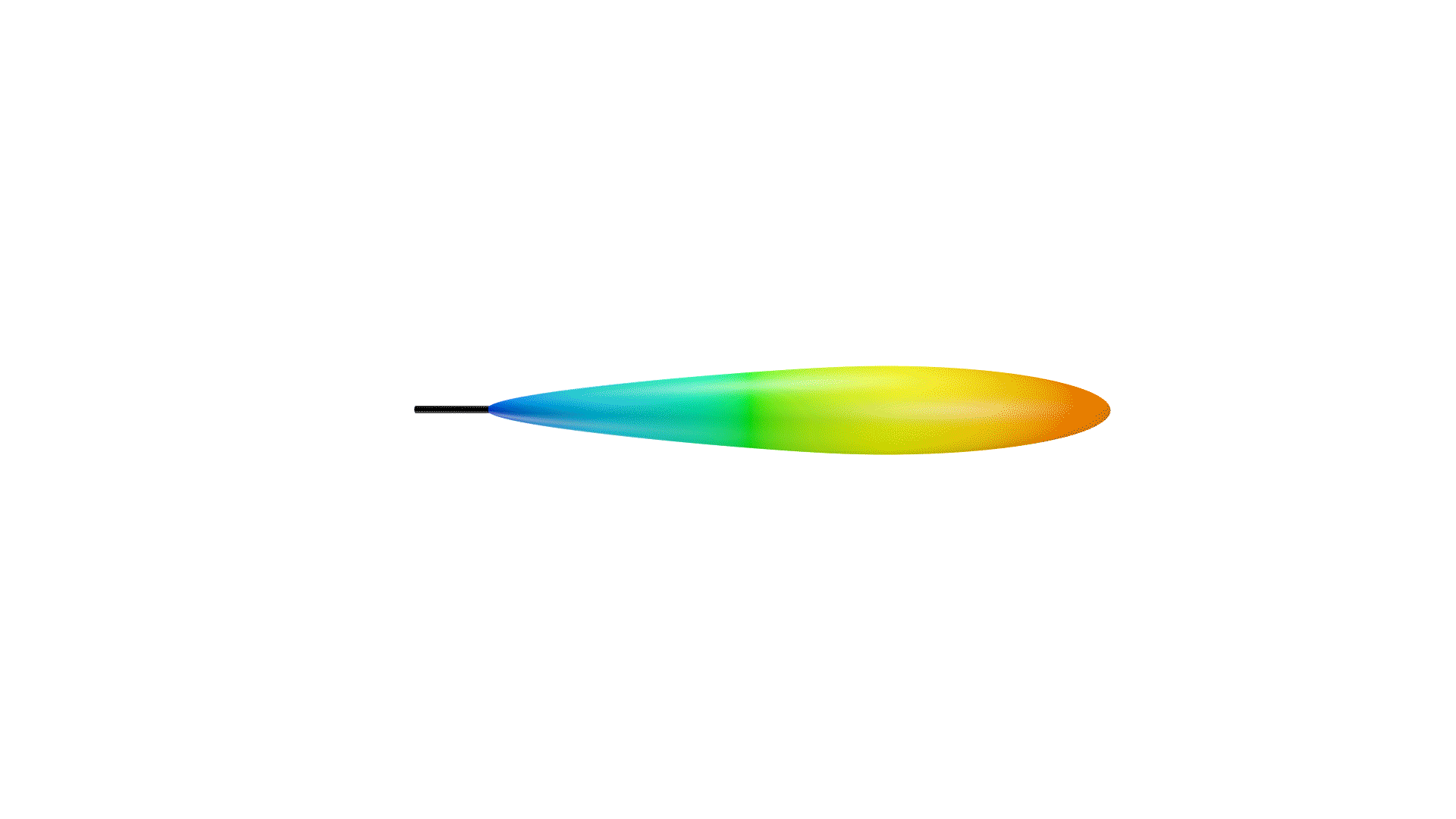
Omnidirectional antennas
On the other hand, Omnidirectional antennas cover 360º of the area, like a donut. This type of antenna is mainly used for outdoor applications to increase signal strength and quality under any conditions. For instance, in a ferry or RV.
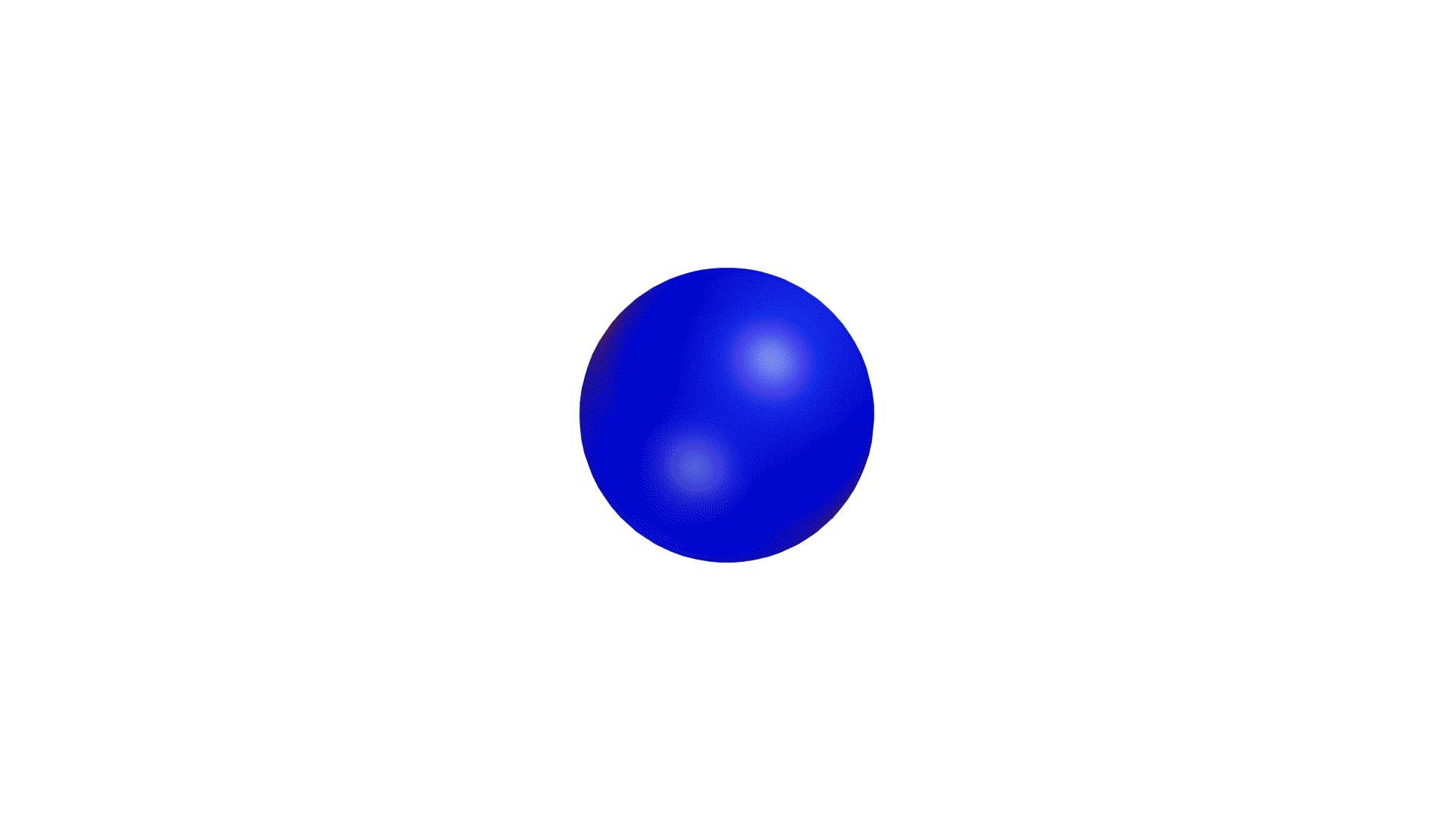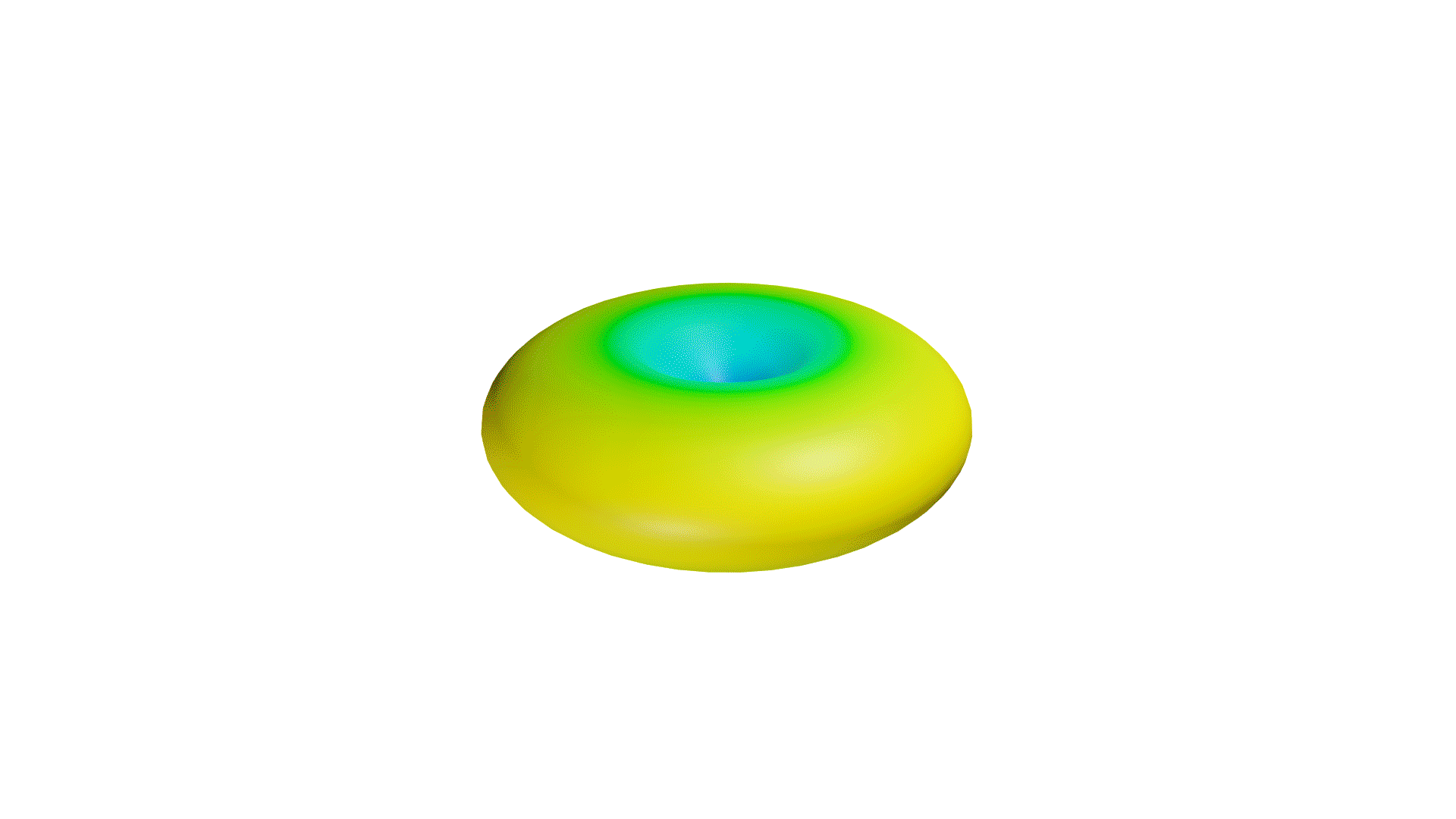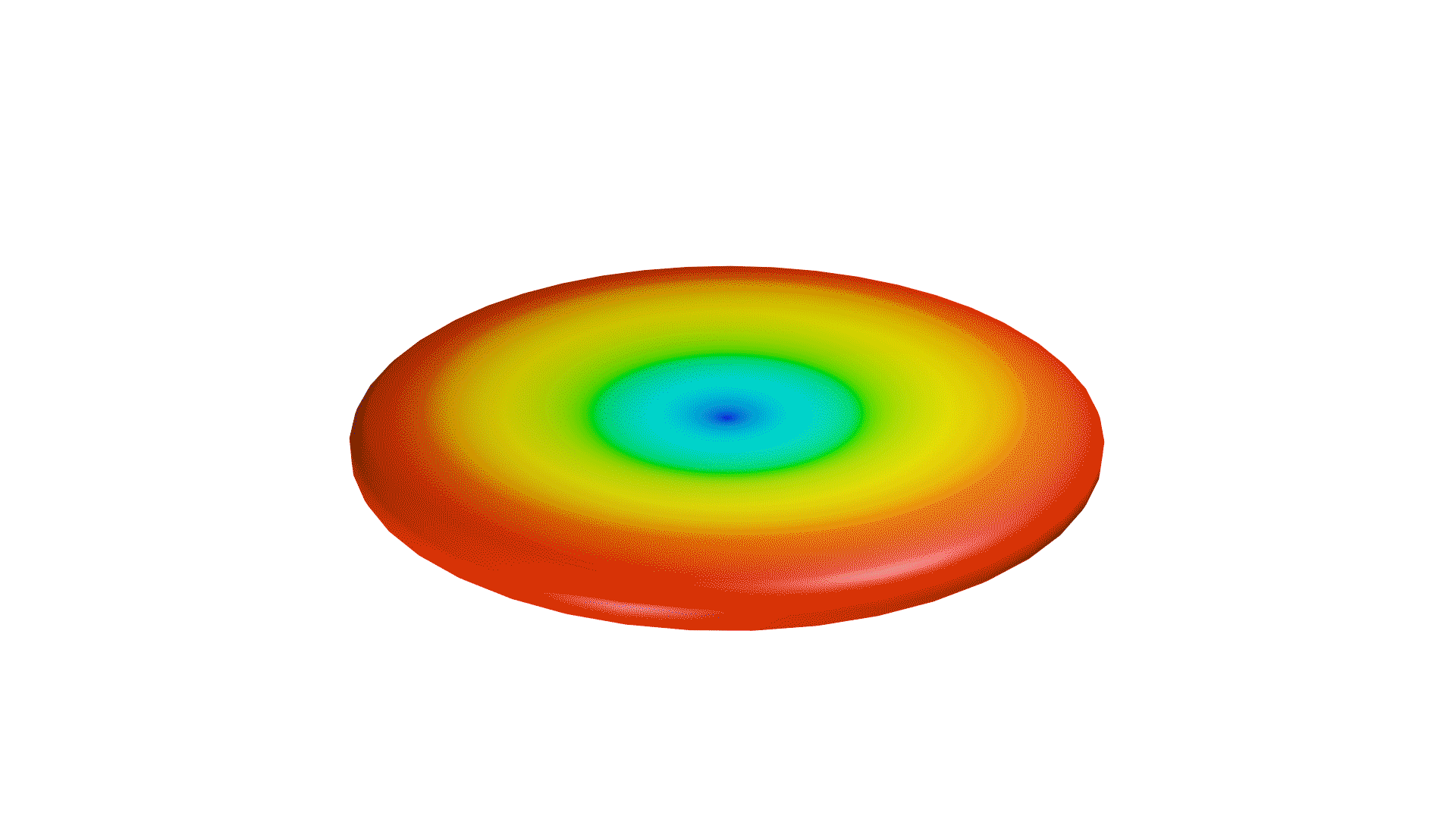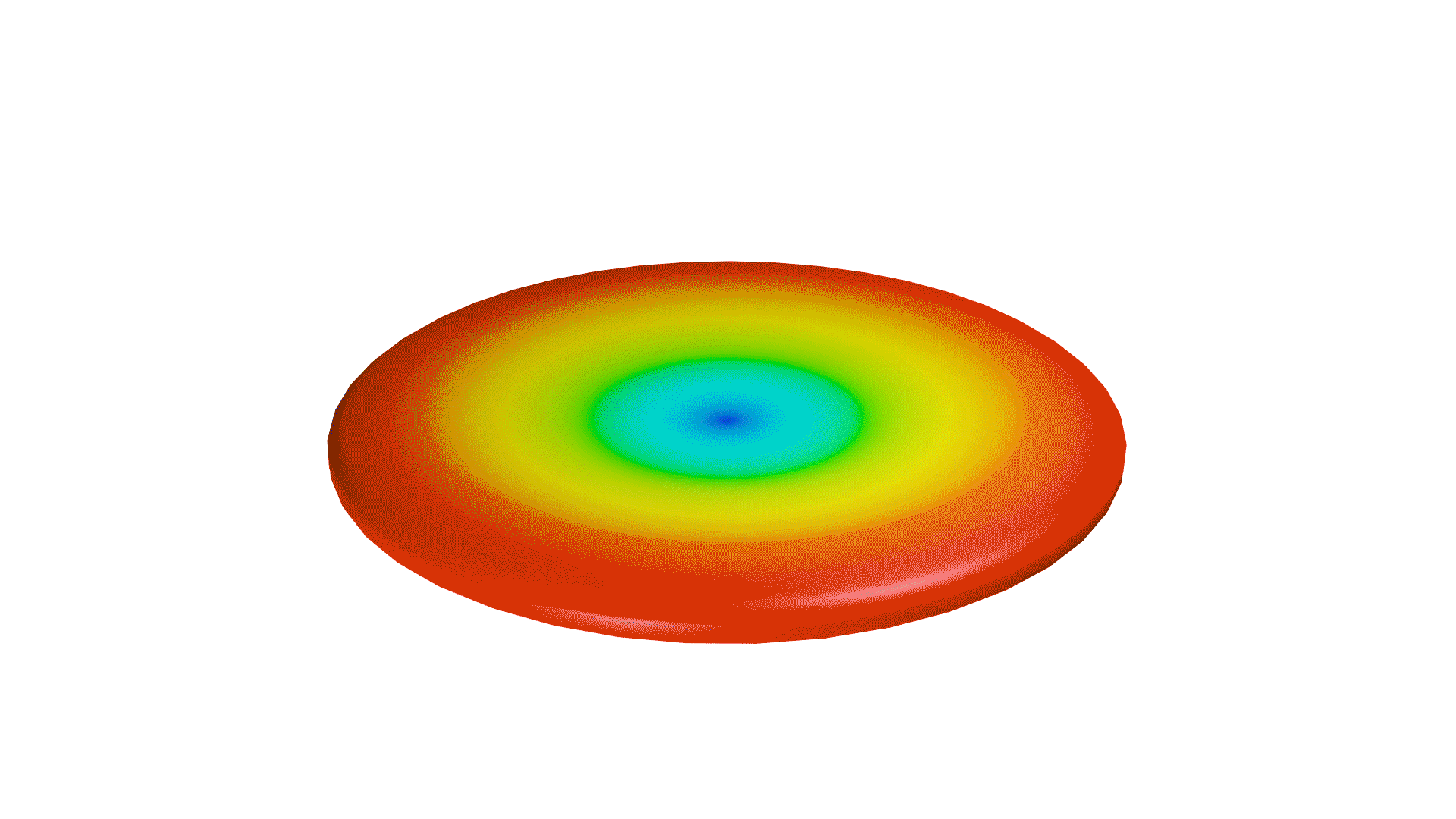
Not only is the directional coverage of an antenna crucial, but so is its gain. If an antenna were a light source, the gain of an antenna would be the focus of a light in a particular direction. When focused on one direction, the light will be brighter in that area, while less light is reflected in other directions.
Directional antennas can be seen as a light torch, with a narrow angle of coverage, but high gain. Omnidirectional antennas, then, are like light bulbs, with greater coverage, but lesser gain. However, similar to directional antennas, the angle of coverage will decrease while the gain is increased.
Choosing an antenna
To choose which antenna is for you, a selection guide for mobile applications includes opting for a high gain omnidirectional antenna. And since it will be used outdoors, an optimal antenna also needs to be sturdy enough to withstand being on the road or at sea.
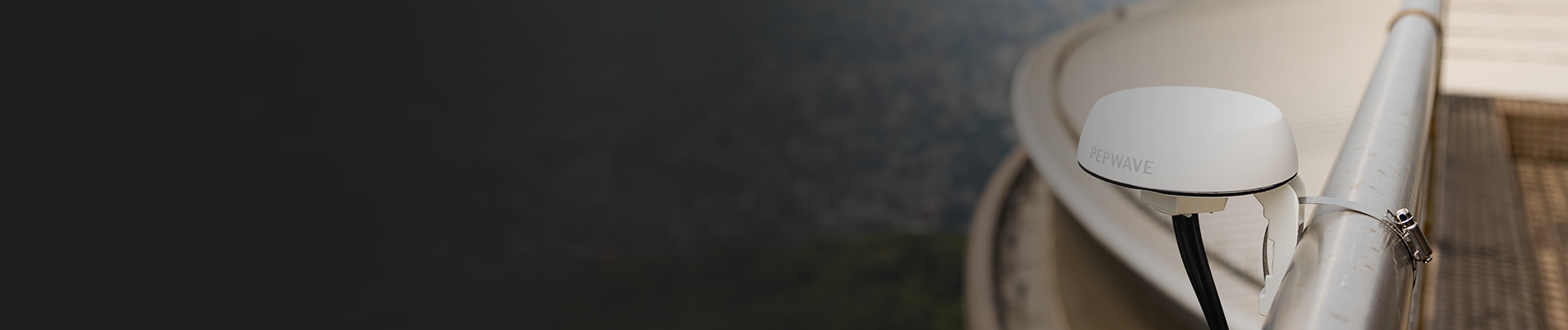

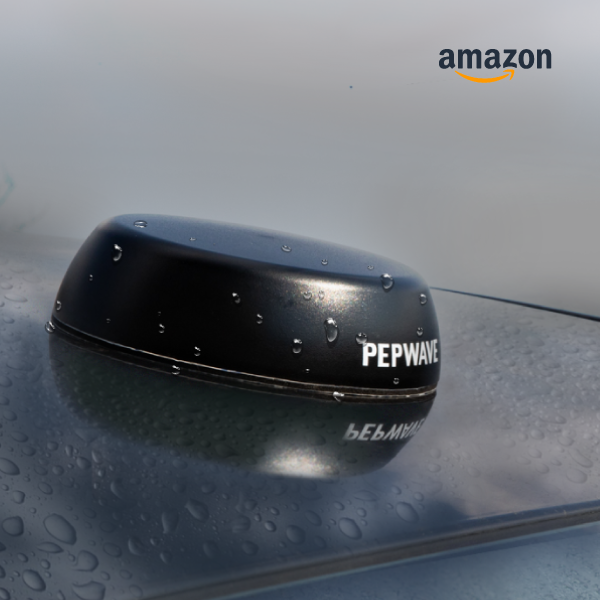
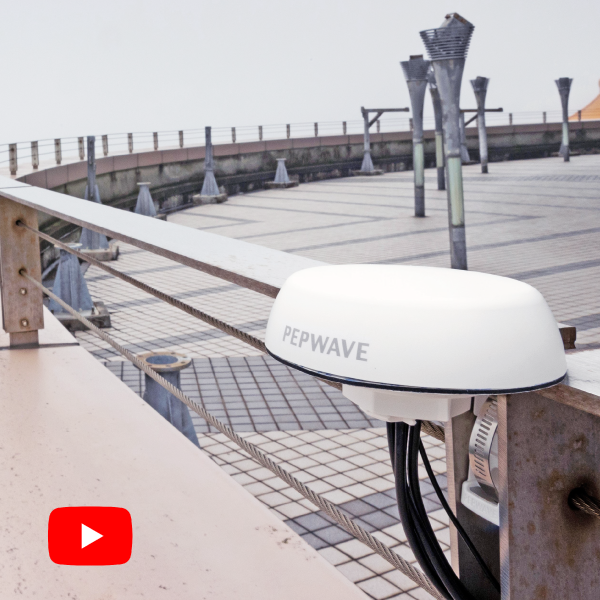
Fulfilling all these criteria, Peplink is introducing their new omnidirectional antenna series, Mobility. Designed for mobile applications, these antennas have high gain and can withstand strong winds with their IP68 rated enclosure, robust design, and exterior made from UV stable plastic. Differentiating themselves from competitors, Peplink’s Mobility antenna series have a wide range of bandwidth, covering virtually all LTE/5G bands.



